Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are making headlines, but how do they actually work? Imagine digital money that doesn’t rely on banks, is secure, and can be sent anywhere in the world. This beginner-friendly guide will walk you through the basics of cryptocurrencies, step by step, so you can understand the technology behind the buzz.
What is a Cryptocurrency?
A cryptocurrency is a type of digital or virtual money that uses cryptography for security. Unlike traditional money (like dollars or euros), cryptocurrencies are decentralized, meaning no government or bank controls them. They exist on a technology called blockchain, a secure digital ledger shared across many computers.
Think of cryptocurrencies as digital cash you can send online without a middleman. Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, was created in 2009, and now thousands of others exist, like Ethereum, Ripple, and Dogecoin.

How Do Cryptocurrencies Work? A Step-by-Step Explanation
Let’s break down how cryptocurrencies function in simple terms:
Step 1: Transactions Are Created
When you send cryptocurrency, like paying someone in Bitcoin, you create a transaction. This transaction includes details like the amount, the sender’s digital address (like an email address), and the receiver’s address. Your transaction is then broadcast to a network of computers.
Step 2: The Blockchain Network Verifies the Transaction
Cryptocurrencies rely on blockchain, a decentralized ledger. Computers in the network, called nodes, verify your transaction using complex math. They check if you have enough funds and if the transaction follows the rules. This ensures no one can spend the same cryptocurrency twice (a problem called double-spending).
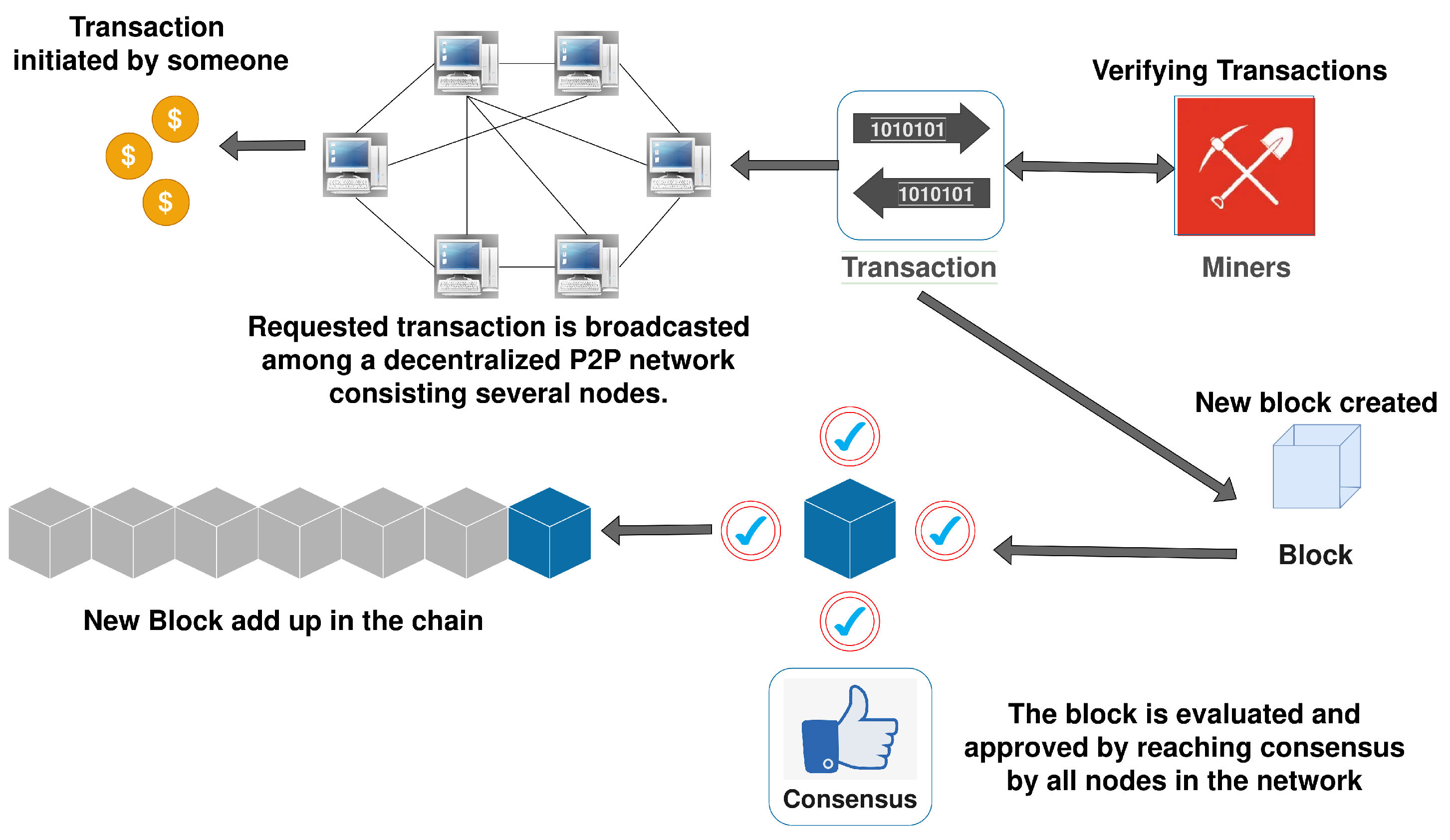
Step 3: Miners or Validators Add the Transaction to the Blockchain
Once verified, the transaction is grouped with others into a “block.” Special network participants, called miners or validators, compete to add this block to the blockchain. For example:
- In Bitcoin, miners solve complex puzzles using powerful computers (this is called Proof of Work).
- In Ethereum, validators stake their own cryptocurrency to confirm transactions (this is called Proof of Stake).
The first to succeed adds the block and earns a reward in cryptocurrency.
Step 4: The Transaction is Complete
Once the block is added to the blockchain, the transaction is permanent and visible to everyone on the network. The recipient now has the cryptocurrency, and the process is complete. This usually takes a few minutes, depending on the cryptocurrency.
Why Are Cryptocurrencies Secure?
Cryptocurrencies are designed to be highly secure, thanks to these features:
- Cryptography: Transactions are encrypted, so only the intended recipient can access the funds.
- Decentralization: The blockchain is stored on thousands of computers, so hacking one won’t compromise the system.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it can’t be changed, preventing fraud.
However, users must protect their private keys (like a password for their cryptocurrency). If someone steals your key, they can access your funds.

What Can You Do with Cryptocurrencies?
Cryptocurrencies are more than just digital money. Here are some common uses:
Payments and Transfers
You can use cryptocurrencies to buy goods, pay for services, or send money globally. For example, some online stores accept Bitcoin, and you can transfer cryptocurrency to someone in another country without high bank fees.
Investing
Many people buy cryptocurrencies as an investment, hoping their value will rise. However, prices can be volatile, so it’s important to research before investing.
Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Some cryptocurrencies, like Ethereum, power DApps—apps that run on blockchain. These include games, financial tools, and even digital art platforms (like NFTs).
Benefits and Risks of Cryptocurrencies
Benefits
- Fast and Cheap Transactions: Sending cryptocurrency across borders is often quicker and cheaper than traditional banking.
- Accessibility: Anyone with an internet connection can use cryptocurrencies, even without a bank account.
- Transparency: Blockchain transactions are public, building trust.
Risks
- Volatility: Cryptocurrency prices can swing wildly, leading to potential losses.
- Security Risks: Losing your private key or falling for scams can result in stolen funds.
- Regulation: Governments are still developing rules for cryptocurrencies, which creates uncertainty.

How to Get Started with Cryptocurrencies
Ready to explore cryptocurrencies? Here’s a simple way to begin:
- Learn the Basics: Understand key terms like wallets, private keys, and exchanges.
- Choose a Wallet: A digital wallet stores your cryptocurrency. Options include software wallets (apps) or hardware wallets (physical devices).
- Buy Cryptocurrency: Use an exchange like Coinbase or Binance to buy cryptocurrency with traditional money.
- Stay Safe: Keep your private keys secure and beware of scams.
Conclusion
Cryptocurrencies are an exciting part of the digital world, offering new ways to pay, invest, and interact online. By understanding how they work—through blockchain, transactions, and security—you can explore this technology with confidence. Start small, do your research, and join the growing community of crypto users shaping the future of money.






















