If you’re new to cryptocurrency, terms like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) might sound intimidating. These are methods blockchains use to secure transactions and create new coins, with PoW often called “mining.” This beginner-friendly guide explains PoW and PoS, how they work, and their differences in simple terms, helping you understand their role in networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum in 2025.

What Are Proof of Work and Proof of Stake?
Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) are consensus mechanisms—rules that blockchains use to agree on valid transactions and keep the network secure. They ensure no one can cheat, like spending the same Bitcoin twice, without needing a central authority like a bank.
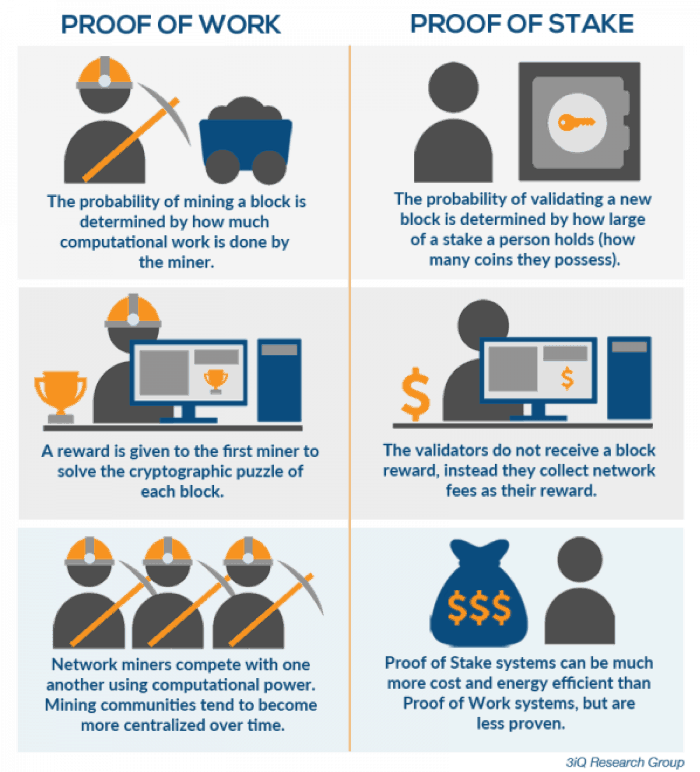
- Proof of Work (PoW): Miners use powerful computers to solve complex math puzzles to validate transactions and earn rewards.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): Validators “stake” their crypto to verify transactions, earning rewards without heavy computing.
Both methods secure blockchains, but they work differently. Let’s break them down.
What is Proof of Work (PoW)?
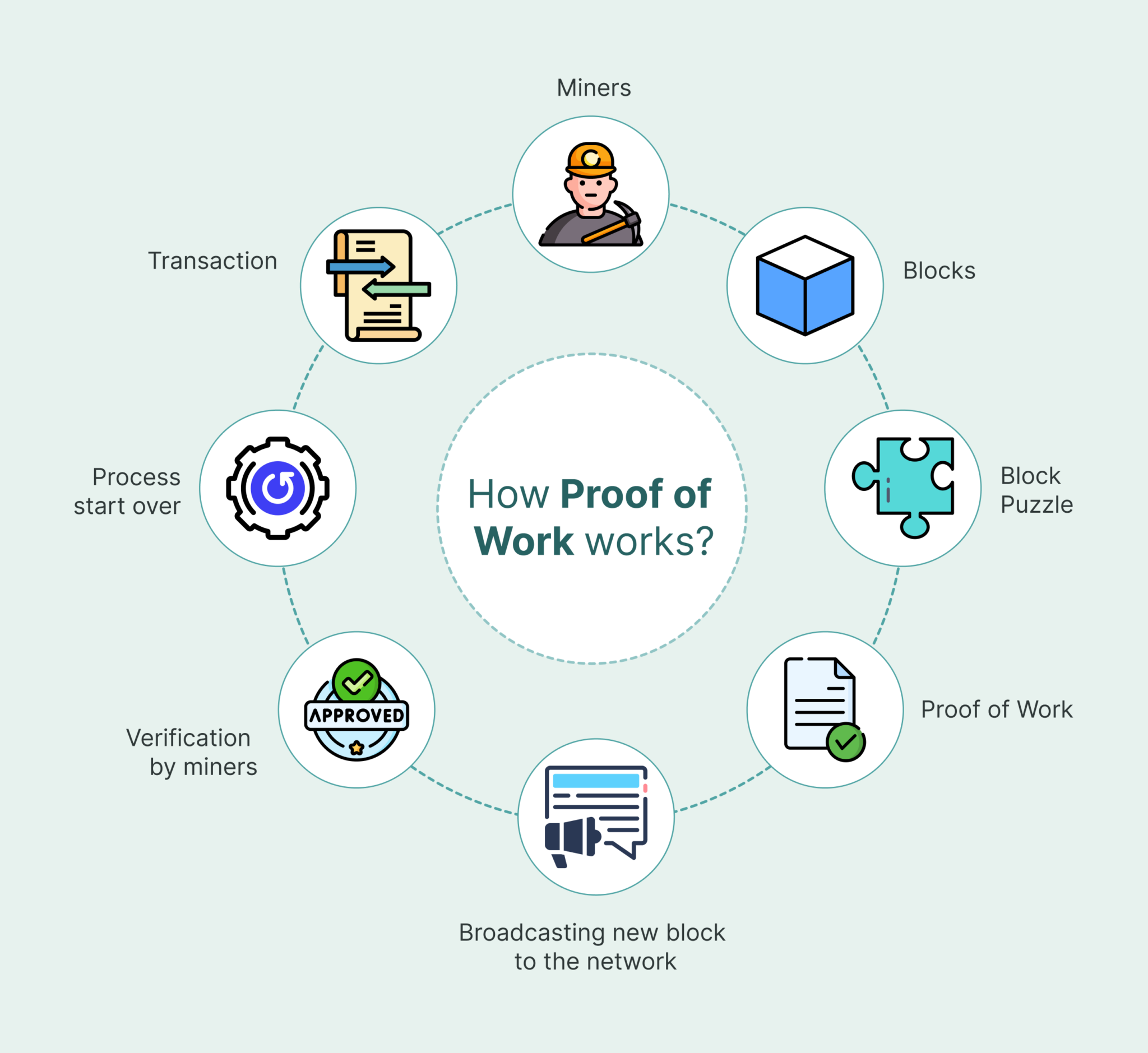
Proof of Work is the original consensus mechanism used by Bitcoin and other early cryptocurrencies. It’s often called “mining” because miners compete to solve puzzles, earning crypto rewards like newly minted Bitcoin.
How It Works:
- Transactions (like sending Bitcoin) are grouped into a block.
- Miners use computers to solve a math puzzle tied to the block.
- The first miner to solve it adds the block to the blockchain.
- The miner earns a reward (e.g., Bitcoin) plus transaction fees.
PoW is like a race where miners use computing power to prove they’ve done the “work” to secure the network.
Pros of Proof of Work
- High Security: Solving puzzles is hard, making it costly for hackers to attack networks like Bitcoin.
- Proven Track Record: Bitcoin has used PoW securely since 2009.
- Decentralized: Miners worldwide keep the network running without a central authority.
Cons of Proof of Work
- Energy Intensive: Mining uses massive electricity, raising environmental concerns.
- High Costs: Expensive hardware (like ASICs) and energy bills make mining less accessible.
- Slower Transactions: PoW can be slower than PoS for processing blocks.
What is Proof of Stake (PoS)?
Proof of Stake is a newer, energy-efficient alternative to PoW, used by blockchains like Ethereum (since 2022) and Cardano. Instead of mining, validators stake their cryptocurrency to verify transactions and earn rewards.
How It Works:
- Validators lock up (stake) a certain amount of crypto, like Ethereum, in the network.
- The blockchain randomly selects validators to verify transactions and create blocks.
- Selected validators confirm the block and add it to the blockchain.
- Validators earn rewards, often a share of transaction fees or new coins.
PoS is like a lottery where staking more crypto increases your chances of being chosen, but everyone plays fair to keep the network secure.

Pros of Proof of Stake
- Energy Efficient: Uses far less electricity than PoW, making it eco-friendly.
- Lower Costs: No need for expensive mining hardware; anyone with crypto can stake.
- Faster Transactions: PoS blockchains often process blocks quicker than PoW.
Cons of Proof of Stake
- Less Proven: PoS is newer, so it has a shorter track record than PoW.
- Wealth Concentration: Those with more crypto have higher chances of validating, potentially favoring the rich.
- Staking Risks: Staked crypto can be locked up or lost if you break rules.
PoW vs. PoS: Key Differences
Here’s a quick comparison to help you understand PoW and PoS:
- Method: PoW uses computing power to solve puzzles; PoS uses staked crypto to validate.
- Energy Use: PoW is energy-heavy; PoS is eco-friendly.
- Cost: PoW requires expensive hardware; PoS needs crypto to stake.
- Speed: PoS is often faster; PoW can be slower.
- Examples: PoW powers Bitcoin; PoS powers Ethereum and Cardano.
Both methods secure blockchains, but PoS is gaining popularity in 2025 for its efficiency. Learn more about blockchain basics at CoinDesk.
Examples of PoW and PoS in Action
Let’s see how these mechanisms work in real cryptocurrencies:
- Bitcoin (PoW): Miners use ASICs to solve puzzles, securing billions in transactions daily. Check Bitcoin’s blockchain on Blockchain.com.
- Ethereum (PoS): Validators stake ETH to confirm transactions, making Ethereum faster and greener since its 2022 upgrade.
- Litecoin (PoW): Similar to Bitcoin, Litecoin uses PoW but with faster block times.
- Cardano (PoS): A popular PoS blockchain known for low fees and eco-friendly validation.
Can Beginners Get Involved?
Both PoW and PoS offer ways for beginners to participate, but they differ in accessibility:
- Proof of Work: Mining requires expensive hardware and high electricity costs, making it tough for beginners. Joining a mining pool like Slush Pool is a more affordable start.
- Proof of Stake: Staking is easier—buy crypto like Ethereum or Cardano on Coinbase and stake it via the platform or a wallet like MetaMask.
Beginner Tip: PoS is more beginner-friendly due to lower costs. Start with staking small amounts to learn without big risks.
How to Start with PoW or PoS
Ready to explore PoW or PoS? Here’s how beginners can begin in 2025:
For Proof of Work (Mining)
- Research coins like Bitcoin or Litecoin to mine.
- Buy hardware (e.g., an ASIC for Bitcoin) or join a pool like F2Pool.
- Install mining software like CGMiner.
- Set up a wallet like Trust Wallet for rewards.
- Monitor electricity costs to ensure profitability.
For Proof of Stake (Staking)
- Buy PoS crypto like Ethereum or Cardano on Binance.
- Transfer to a wallet like MetaMask or stake directly on the exchange.
- Choose a staking pool or validator to join.
- Lock your crypto to start earning rewards.
- Secure your wallet with 2FA and a hardware device like Ledger.
Challenges of PoW and PoS
Both systems have drawbacks beginners should understand:
- PoW Challenges: High energy use, expensive hardware, and environmental concerns make mining less sustainable.
- PoS Challenges: Staking locks up funds, and there’s a risk of losing crypto if validators misbehave. PoS is also less battle-tested than PoW.
Research both methods on CoinDesk to make informed choices.
Tips for Beginners
Explore PoW and PoS safely with these tips:
- Start Small: Mine or stake with small amounts to learn without big risks.
- Secure Your Crypto: Use a hardware wallet like Ledger and never share your seed phrase.
- Avoid Scams: Beware of fake mining or staking platforms promising guaranteed profits.
- Stay Informed: Follow crypto news on Cointelegraph for 2025 trends.
Conclusion
Proof of Work and Proof of Stake are the backbone of cryptocurrency networks, securing blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum in different ways. PoW’s mining is secure but energy-heavy, while PoS’s staking is eco-friendly and beginner-friendly. By understanding their differences, you can explore mining or staking with confidence in 2025. Start small with a pool like Slush Pool or staking on Coinbase, and discover how these mechanisms power the crypto world!






















