Blockchain networks like Ethereum and Bitcoin are secure and decentralized, but they face a big challenge: scalability. As more users join, transaction speeds slow down, and costs rise. Sharding is a game-changing solution that promises to make blockchains faster and more efficient. This beginner-friendly guide explains what sharding is, how it works, and why it’s critical for the future of blockchain. Let’s dive in!

What Is Sharding?
Sharding is a technique that splits a blockchain into smaller, manageable pieces called shards. Each shard processes its own transactions and smart contracts, allowing the network to handle more work simultaneously. Think of it like dividing a busy restaurant into multiple sections, each with its own staff, so more customers can be served at once.
Without sharding, every node (computer) in a blockchain network must process every transaction, which slows things down as the network grows. Sharding spreads the workload, boosting speed and scalability.
Why Sharding Matters for Blockchain
Blockchains face a scalability trilemma: balancing decentralization, security, and scalability. Most networks excel at two but struggle with the third. For example:
- Bitcoin: Secure and decentralized but slow (~7 transactions per second).
- Ethereum: Supports complex DApps but gets congested, raising gas fees.
Sharding aims to solve this by enabling blockchains to process thousands of transactions per second without sacrificing security or decentralization.
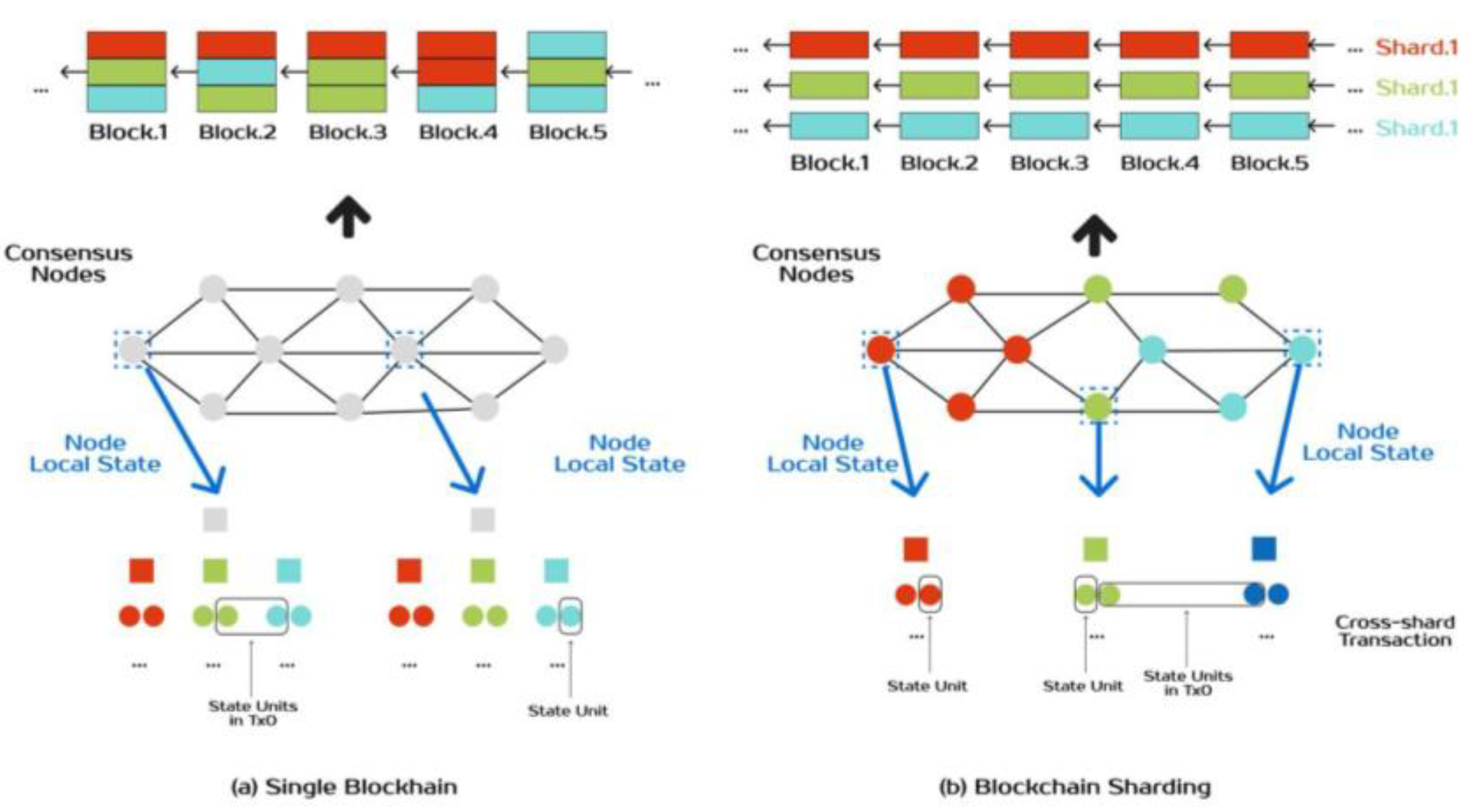
How Sharding Works: A Technical Breakdown
Sharding divides a blockchain’s data and workload into smaller partitions. Here’s a step-by-step look at how it works:
1. Splitting the Blockchain
The blockchain’s state (e.g., account balances, smart contracts) is divided into multiple shards. Each shard is like a mini-blockchain with its own transactions and data. For example, Shard A might handle transactions for accounts 1–100, while Shard B covers accounts 101–200.
2. Assigning Nodes to Shards
Nodes are assigned to specific shards, so they only process transactions for their shard. This reduces the computational load on each node, making the network faster. Nodes can still validate other shards’ data to maintain security.
3. Cross-Shard Communication
Shards need to “talk” to each other for transactions that span multiple shards (e.g., sending ETH from Shard A to Shard B). A beacon chain or main chain coordinates these interactions, ensuring consistency across the network.
4. Maintaining Security
Sharding introduces risks, like a single shard being compromised. To prevent this, blockchains use techniques like random shard assignment (nodes are shuffled regularly) and cross-shard validation to ensure no shard can be easily attacked.
Sharding in Ethereum: A Real-World Example
Ethereum, one of the most popular blockchains, is implementing sharding as part of its scalability roadmap (post-2022 Merge). Here’s how it works:
- Beacon Chain: Introduced in 2020, it coordinates shards and manages validators in Ethereum’s Proof of Stake (PoS) system.
- Shard Chains: Ethereum plans to create multiple shards, each handling a subset of transactions and smart contracts.
- Rollups Integration: Sharding works with layer-2 solutions like Optimism, which process transactions off-chain and settle them on shards, boosting speed further.
Ethereum’s sharding aims to increase its capacity to tens of thousands of transactions per second, making DApps like DeFi and NFTs more affordable and accessible.

Benefits of Sharding
Sharding offers several advantages for blockchain networks:
- Faster Transactions: Parallel processing across shards increases throughput.
- Lower Costs: More transactions per second reduce gas fees, benefiting users.
- Better Scalability: Networks can handle growing demand without slowing down.
- Improved Accessibility: Nodes need less storage and computing power to participate, encouraging decentralization.
Challenges of Sharding
While promising, sharding isn’t perfect. Here are some hurdles:
- Complexity: Coordinating shards and ensuring cross-shard communication is technically challenging.
- Security Risks: Individual shards are easier to attack than a full blockchain, requiring robust safeguards.
- Data Consistency: Ensuring all shards stay in sync (e.g., correct account balances) is tricky.
Projects like Ethereum are addressing these with careful design and testing.
Sharding vs. Other Scalability Solutions
Sharding isn’t the only way to scale blockchains. Here’s how it compares to alternatives:
- Layer-2 Rollups: Solutions like Arbitrum process transactions off-chain and settle them on the main chain. They’re faster but rely on the main chain’s security.
- Sidechains: Independent blockchains (e.g., Polygon) linked to the main chain. They’re flexible but less secure than sharding.
- Off-Chain Solutions: State channels (e.g., Lightning Network) handle transactions privately, but they’re limited to specific use cases.
Sharding is unique because it scales the blockchain itself (layer-1), preserving decentralization and security while complementing layer-2 solutions.
Other Blockchains Using Sharding
Besides Ethereum, other blockchains are exploring sharding:
- Zilliqa: One of the first to implement sharding, processing transactions in parallel shards.
- NEAR Protocol: Uses “Nightshade” sharding to achieve high throughput for DApps.
- Polkadot: Employs a sharding-like model with “parachains” for specialized tasks.
Each project adapts sharding to its needs, showcasing its versatility.
How Sharding Impacts Developers and Users
For Developers: Sharding simplifies DApp development by reducing gas fees and speeding up transactions. However, developers must design contracts to handle cross-shard interactions, which adds complexity.
For Users: Sharding means cheaper, faster DApps, making DeFi, NFTs, and gaming more accessible. Users won’t notice sharding directly but will enjoy a smoother experience.
Resources for Learning More
Want to dive deeper into sharding? Check out these resources:
- Ethereum Docs: Sharding details at ethereum.org.
- Zilliqa Whitepaper: Sharding implementation at docs.zilliqa.com.
- Blockchain Communities: Join discussions on Ethereum Stack Exchange or NEAR’s forums.
Stay curious and explore sharding’s evolving role in blockchain.
Conclusion
Sharding is a powerful solution to blockchain’s scalability challenges, splitting networks into manageable shards to process transactions faster and cheaper. While complex, it’s key to making blockchains like Ethereum ready for mass adoption. By understanding sharding’s mechanics, benefits, and challenges, you’re better equipped to navigate the future of decentralized tech.
What do you think about sharding’s potential? Share your thoughts in the comments below!






















